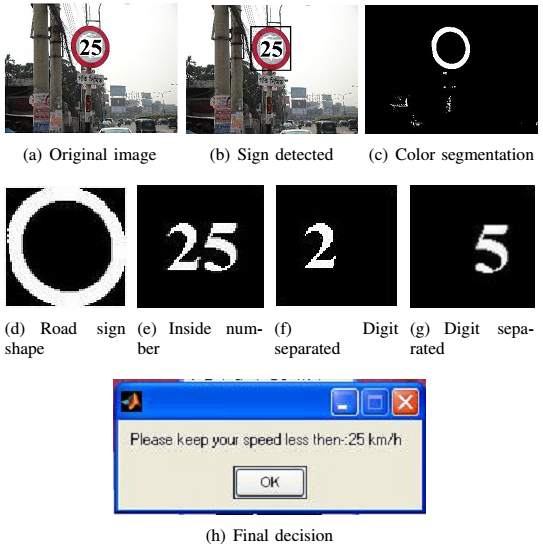
Incremental Activity Modeling.
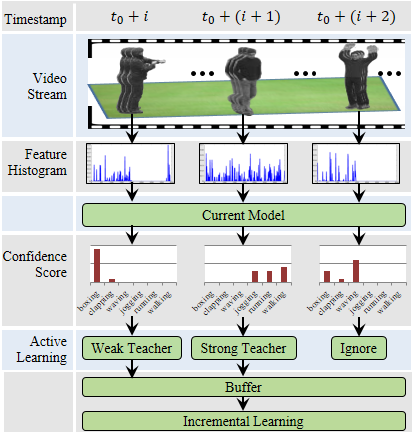
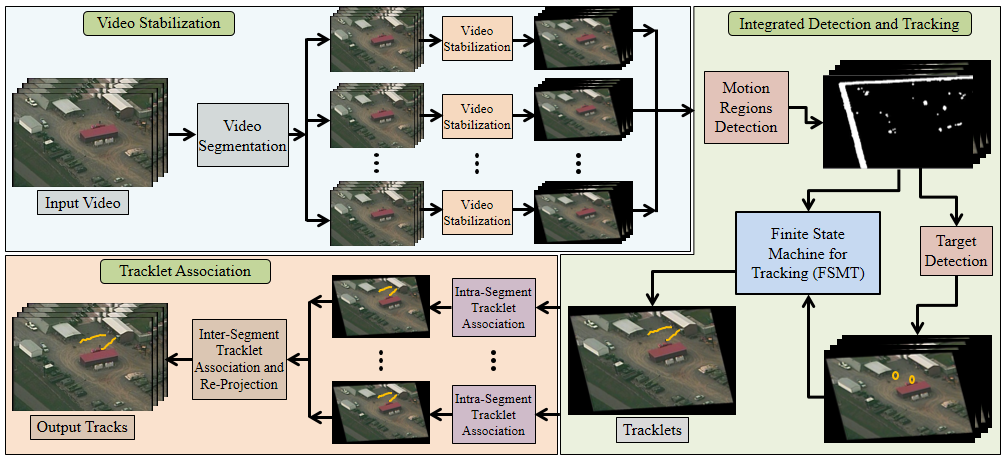
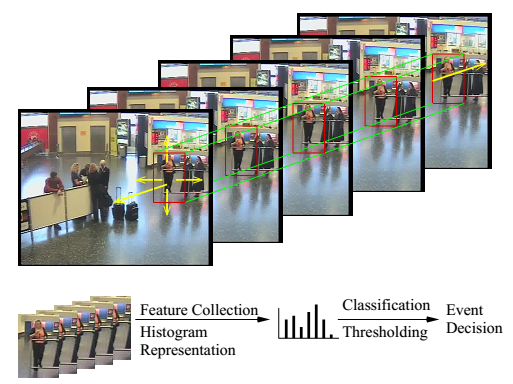
Human activity recognition in videos is a difficult but widely studied problem in computer vision due to its numerous practical applications. Most of the state-of-the-art approaches to human activity recognition need an intensive training stage and assume that all of the training examples are labeled and available beforehand. But these assumptions are unrealistic for many applications where we have to deal with streaming videos. In these continuous streaming videos, as new activities are seen, they can be leveraged upon to improve the current activity recognition model. In this work, we aim to develop an incremental activity learning framework that will be able to continuously update the activity models and learn new ones as more videos are seen. Our proposed approach leverages upon state-of-the-art machine learning tools, most notably active learning systems, and leads to the development of an online activity recognition framework for streaming videos. It does not require tedious manual labeling of every incoming examples of each activity class. We perform rigorous experiments on challenging human activity datasets, which demonstrate the robustness of our incremental activity modeling framework